AI for Businesses
Notes on AI in businesses
###Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the ability of a computer program or machine to mimic human-like behavior. For example:
- >Mimicking visual senses
- >Speech recognition
- >Decision-making
- >Natural language understanding
AI is not a technology by itself but a goal set by technologists to imitate human intelligence.
###What is Data Science?
Data science is an interdisciplinary field aimed at achieving AI. It primarily uses machine learning and statistics techniques. In most cases, data scientists are experts responsible for solving AI-related problems.
###What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a technique where a machine sifts through enormous amounts of data to find patterns.
- >This technique is frequently used for AI purposes.
- >Machine learning uses algorithms to train a machine to learn patterns based on differentiating features about the data.
- >The more training data, the more accurate the predictions.
###What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning.
- >It imitates how the human brain processes information through a connected artificial neural network.
- >Unlike traditional machine learning, deep learning can discover complex patterns and differentiating features about the data independently.
###Everyday AI
Numerous AI capabilities are already integrated into everyday applications, addressing realities such as:
- >Virtual communication
- >Managing overwhelming amounts of information
These capabilities are present across almost every job and function.
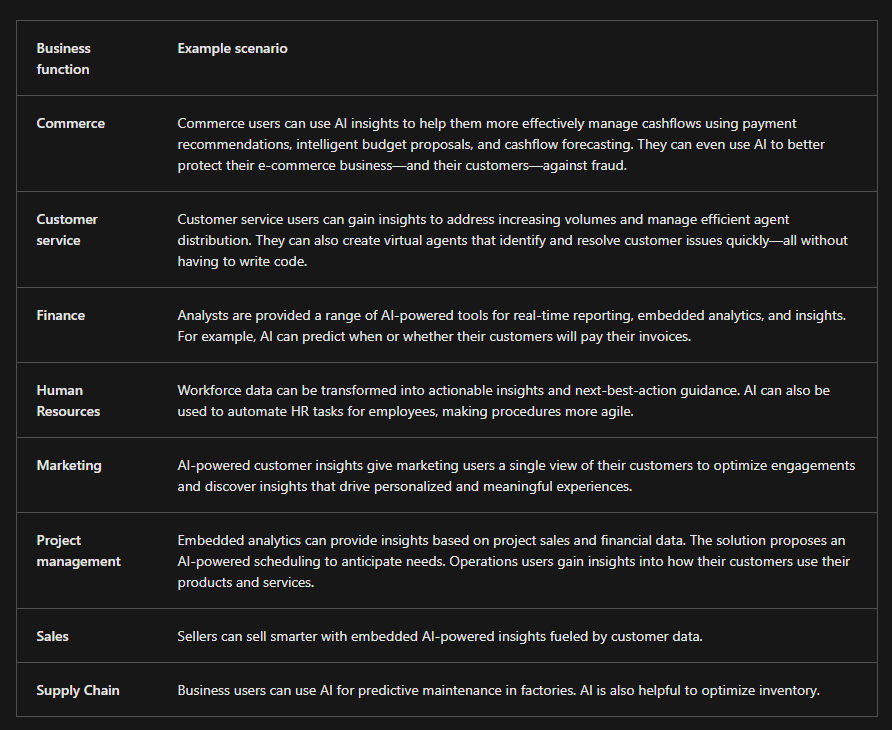
###Business Functions for Everyday AI
###Characteristics That Foster an AI-Driven Culture
A successful AI strategy addresses cultural and business issues. Fostering an AI-driven culture requires:
- >Being data-driven
- >Empowering people
- >Creating a responsible approach to AI
1. Data-Driven
- >AI systems rely on high-quality and complete data.
- >Organizations need access to their entire data estate for reasoning.
2. Data Access
- >Most organizations generate and use data in silos.
- >Unified data provides better visibility for operational efficiency.
3. Data Integrity
- >Errors like inaccurate, irrelevant, or duplicate data reduce effectiveness.
- >Quality and integrity are critical to prevent errors.
4. Empowered
Empowering employees enables cross-functional collaboration for AI transformation.
5. Responsible
As AI evolves, it poses complex societal and ethical challenges. A responsible approach ensures AI aligns with desired futures.
###AI Systems for Governance
To implement governance for AI, organizations can:
1. Make Resources Available

- >Employees need guidance (e.g., handbooks, manuals, training sessions) to incorporate responsible AI principles.
2. Create a Centralized AI Inventory

- >Maintain a list of all AI models/systems in use.
- >Helps prioritize efforts and optimize resources.
3. Develop Tools

- >Automate compliance monitoring for performance validation.
- >Alert systems when performance metrics deviate.
###Scaling AI in Organizations
Adopting AI requires significant investments and a long-term perspective.
###What is Microsoft's Horizon-Based Framework?
Microsoft uses a horizon-based framework to evaluate and prioritize AI investments. This framework divides development into phases:
Horizon 1: Running (Operate and Optimize the Core Business)
- >Focus: Automate or improve existing processes.
- >Example:
- >A manufacturer using AI for quality checks could increase efficiency (e.g., inspecting 1,000 parts/hour vs. 100 manually).
Horizon 2: Growing (Improve Market Position)
- >Focus: Create new services or customer experiences.
- >Example:
- >A manufacturer using IoT and AI to suggest optimal maintenance schedules.
Horizon 3: Transforming (Change Market Position)
- >Focus: Revolutionize business models and create new markets.
- >Example:
- >Developing innovative AI solutions that cross industry boundaries or create new customer needs.