AI Fundamentals
Notes on AI Fundamentals
###Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Simply put, AI is software that imitates human behaviors and capabilities. Key workloads within AI include:
- >i. Machine Learning: The foundation for most AI systems, machine learning is how we "teach" a computer model to make predictions and draw conclusions from data.
- >ii. Computer Vision: Capabilities within AI that allow it to interpret the world visually through cameras, video, and images.
- >iii. Natural Language Processing: Capabilities within AI that enable a computer to interpret written or spoken language and respond accordingly.
- >iv. Document Intelligence: AI capabilities that manage, process, and use high volumes of data found in forms and documents.
- >v. Knowledge Mining: AI capabilities that extract information from large volumes of often unstructured data to create a searchable knowledge store.
- >vi. Generative AI: Capabilities within AI that create original content in a variety of formats, including natural language, images, code, and more.
###Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning is the foundation for most AI solutions. Since the 1950s, researchers—often known as data scientists—have developed different approaches to AI. Most modern applications of AI have their origins in machine learning, a branch of AI that combines computer science and mathematics.
Machine learning models try to capture the relationship between data, helping machines make predictions based on patterns.
###Computer Vision
Computer Vision is an area of AI that deals with visual processing, allowing machines to interpret and analyze visual data from the world through images or videos.
###Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing (NLP) is an area of AI that focuses on creating software that understands written and spoken language, enabling better communication between humans and machines.
###Document Intelligence
Document Intelligence is the area of AI that handles managing, processing, and utilizing high volumes of data found in forms and documents. It involves extracting and interpreting data from structured and unstructured sources.
###Generative AI
Generative AI describes a category of AI capabilities that create original content. People typically interact with generative AI that has been integrated into chat applications, generating responses, text, images, and even code based on user input.
###Threats & Risks of AI
AI technologies come with their own set of risks and challenges:
- >Bias: AI systems may produce biased results, often reflecting the biases in the training data.
- >Errors: Mistakes in AI decision-making can have harmful consequences, especially when AI systems are used in critical sectors.
- >Data Exposure: AI systems could unintentionally expose personal or sensitive information, leading to data leaks or privacy violations.
- >Solution-less Problems: There are still many problems that AI cannot yet solve, including ethical dilemmas and complex real-world scenarios.
- >Trust in Complex Systems: As AI systems become more complex, they may become less understandable, leading to difficulty in building trust in their decisions.
- >Liability: Determining who is liable for AI-based decisions and their consequences can be a challenge.
###Responsible AI
Developing AI-based systems with responsibility is essential. Some principles for developing ethical AI include:
- >i. Fairness: AI systems should treat all people fairly, without discrimination.
- >ii. Reliability & Safety: AI systems should perform reliably and safely in all intended scenarios.
- >iii. Privacy & Security: AI systems should respect privacy and ensure that sensitive data is secure.
- >iv. Inclusiveness: AI systems should empower everyone, engaging people from diverse backgrounds and experiences.
- >v. Transparency: AI systems should be understandable, with clear explanations of how decisions are made.
- >vi. Accountability: People should be accountable for the actions and outcomes of AI systems.
###Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning has its roots in statistics and mathematical modeling of data. The fundamental idea is to use data from past observations to predict unknown outcomes or values, enabling AI systems to make better decisions.
###Types of Machine Learning
There are multiple types of machine learning, and the appropriate type should be selected depending on the problem at hand.
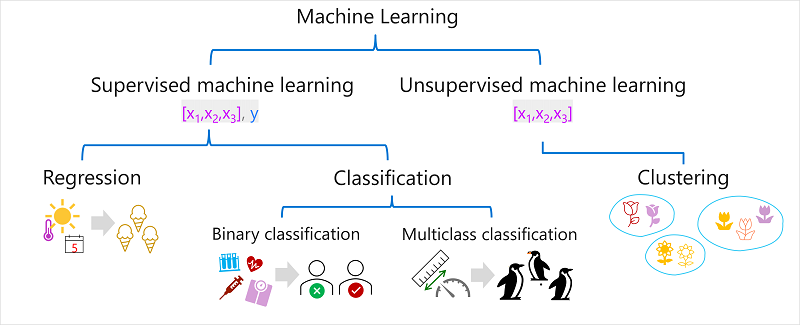
1. Supervised Machine Learning
Supervised machine learning is a general term for algorithms where the training data includes both feature values and known label values.
- >i. Regression: A form of supervised machine learning where the model predicts a numeric label.
- >ii. Classification: A form of supervised machine learning where the label represents a category or class. Common scenarios include:
- >a. Binary Classification: Predicts whether an item is or isn't part of a specific class.
- >b. Multiclass Classification: Extends binary classification to predict one of multiple possible classes.
2. Unsupervised Machine Learning
Unsupervised machine learning involves training models with data consisting only of feature values, without known labels. These algorithms find relationships and patterns among the features.
- >i. Clustering: A common form of unsupervised machine learning where a clustering algorithm groups data points with similar features together into discrete clusters.