Introduction to OSINT by Security Blue Team
Introduction to OSINT
##What is OSINT?
Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) refers to information gathered from publicly accessible sources. It plays a critical role in law enforcement, cybercrime activities, and business operations such as market research and competitive analysis.
###Examples of OSINT Data
- >
Employee Information on Public Websites
Pages like "Meet the Team" can expose contact details, aiding attackers in social engineering schemes. - >
Job Descriptions Revealing Internal Systems
A job listing mentioning expertise in Windows Server 2016 and Solaris can guide attackers in planning privilege escalation or lateral movement. - >
Geotagged Photos with Metadata
Photos shared online often contain metadata like location and device details, which attackers can extract within seconds. - >
Social Media Profiles
Personal information like birthdates, interests, and connections can aid in crafting targeted social engineering attacks. - >
Tracking Cybercriminals
OSINT supports threat intelligence, helping uncover cybercriminals' identities and aiding law enforcement efforts.
##Why is OSINT Useful?
###For Defenders
Defenders use OSINT to reduce the attack surface by:
- >Assessing public exposure, such as employee social media posts or old login portals.
- >Training employees to identify and resist social engineering attempts.
- >Removing sensitive information from public platforms.
###For Law Enforcement
OSINT enables authorities to:
- >Track criminals, suspects, and terrorists.
- >Build profiles and predict movements using behavioral data.
###For Businesses
Organizations benefit from OSINT by:
- >Monitoring competitors and market trends.
- >Enhancing customer engagement through data analysis.
- >Identifying risks like leaked credentials or insider threats.
###For Attackers
OSINT assists attackers in passive reconnaissance by:
- >Identifying systems and vulnerabilities.
- >Planning exploits.
- >Crafting personalized attacks.
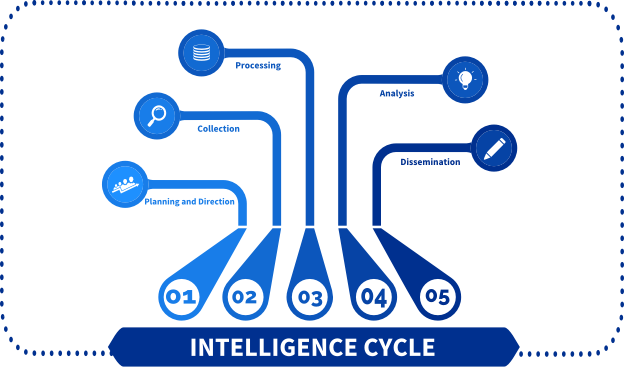
##The Intelligence Cycle
The Intelligence Cycle transforms raw data into actionable insights through these stages:
- >
Planning and Direction
Define research objectives and determine required information. - >
Collection
Use techniques to gather relevant data. - >
Processing
Decode, validate, and filter the collected data for usability. - >
Analysis
Interpret and compile data into actionable insights. Present findings in a report or presentation. - >
Dissemination
Share insights with stakeholders for informed decision-making.
##Online Tracking
Despite popular belief, OSINT activities often leave digital traces. It's vital to manage your digital footprint during operations.
###Fingerprinting
IP Addresses
IP addresses can reveal your identity. Use tools to mask your IP while conducting sensitive research.
Cookies
Cookies, especially third-party tracking cookies, store data to monitor user activity across platforms.
Browser Fingerprinting
Web browsers generate unique identifiers from system data (e.g., OS, screen resolution). Websites use these to recognize and track devices.
- >Test your browser's anonymity: Cover Your Tracks
##Anonymization
While complete online anonymity is impossible, you can minimize your exposure with these steps:
- >
Use Secure Systems
- >Opt for virtual machines (VMs) or a Linux Live ISO to ensure trace-free operations.
- >Tools:
- >
Hide Your IP
- >Use a VPN or the Tor Browser to mask your public IP and encrypt traffic.
- >
Install Privacy Extensions
- >User-Agent Switcher and Manager: Spoof browser identifiers.
- >uBlock Origin: Block ads and unauthorized tracking scripts.
##Tools & Services
###The Harvester
A command-line OSINT tool to gather information like:
- >Hostnames
- >IP addresses
- >Emails
Example Usage:
git clone https://github.com/laramies/theHarvester
cd theHarvester
python3 theHarvester.py -d qualys.com -l 100 -b anubis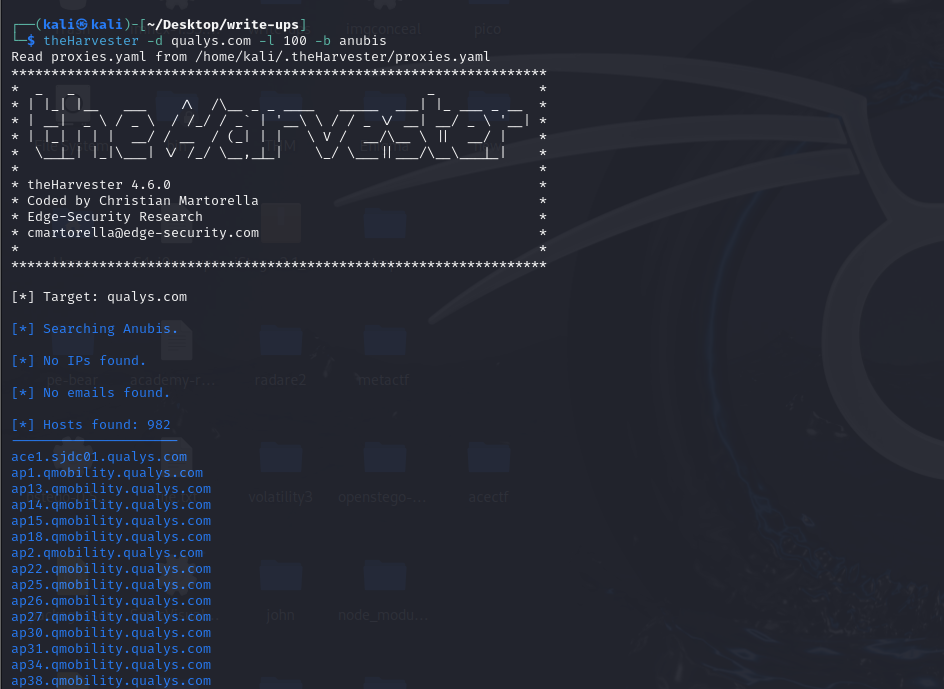
###Maltego
A data mining tool to visualize connections between entities like companies, people, and websites. Simply type
in the command line to start.maltego
###Tweetdeck
Monitor real-time events like vulnerabilities or cyberattacks. If Tweetdeck is unavailable, consider using Twint as an alternative.
###Google Dorking
Leverage Google’s advanced search operators (
) for:operator:keyword
- >Finding files (e.g.,
)filetype:pdf - >Exposing hidden login portals (e.g.,
)inurl:admin - >Enumerating subdomains (e.g.,
)site:example.com -site:www.example.com
Learn more: Google Dorks Guide
Defending Against Google Dorks
- >
IP Whitelisting and Geofencing
Restrict content access to authorized IPs. - >
Crawler Restrictions
Add a
file to block search engine indexing:robots.txttxtUser-agent: * Disallow: / - >
Content Removal
Request Google to remove sensitive information from search results.
##Additional Tools
###OSINT Framework
A curated list of OSINT tools: OSINT Framework
###TinEye
Image recognition tool to track the online usage of your images: TinEye
###Google Image Search
Search for visually similar images or locate image sources: Image Search