Tools of the trade - Linux and SQL
Informational notes for Google Cybersecurity Professional Course - Tools of the Trade
###Operating Systems (OS)
The OS serves as the interface between computer hardware and users. It ensures efficiency and ease of use by managing computer operations.
###Key Concepts
Hardware
The physical components of a computer.
Application
A program that performs a specific task.
- >Applications send requests to the OS, which forwards them to the hardware.
- >Hardware communicates back to the OS, which relays information to applications.
Boot Process
When a computer is turned on:
- >BIOS/UEFI:
- >BIOS: Prevalent in older systems, it contains loading instructions.
- >UEFI: A modern replacement for BIOS, more advanced and flexible.
- >Bootloader: Software that loads the operating system.
Resource Allocation
The OS manages memory and resources to optimize CPU usage across multiple tasks and processes.
Virtual Machines and Virtualization
- >Virtual Machine (VM): A virtual representation of a physical computer.
- >Virtualization: Creating virtual versions of machines using software.
Interfaces
- >User Interface: Allows users to control OS functions.
- >Graphical User Interface (GUI): Uses visual icons (e.g., Start menu, Taskbar).
- >Command Line Interface (CLI): Text-based interaction via commands.
###Linux Overview
An open-source operating system derived from UNIX.
Linux Components
- >User: Interacts with the system.
- >Applications: Perform specific tasks.
- >Shell: Command-line interpreter.
- >Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS): Organizes data.
- >Kernel: Manages processes and memory.
- >Hardware: Physical components.
Popular Linux Distros
- >
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (CentOS)
- >
Slackware (SUSE)
- >
Debian (Ubuntu, Kali Linux)
File-Permissions-Linux
Linux Commands
- >
: Prints current directory.pwd - >
: Lists files and directories.ls - >
: Changes directory.cd - >
: Searches a file for specified strings.grep - >
: Creates directories.mkdir - >
: Removes files or directories.rm - >
: Moves files.mv - >
: Changes file permissions.chmod
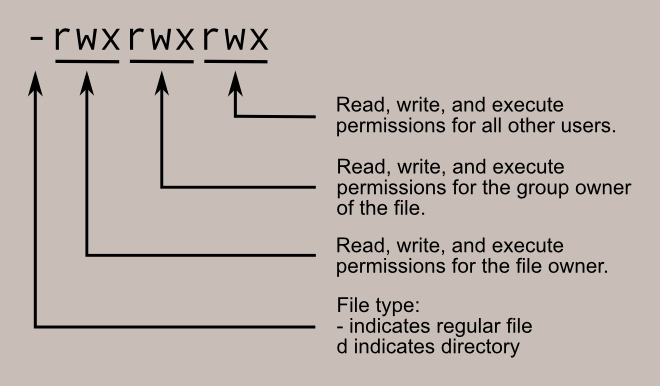
File Permissions
- >Types: Read (r), Write (w), Execute (x).
- >Owners: User (u), Group (g), Others (o).
Basic Shells
- >Bash: Most common.
- >Zsh: Enhanced features.
- >Csh/Ksh: Older alternatives.
###Security Analysts and Linux
- >Analyze logs, manage files remotely, and configure permissions.
- >Use commands and tools like
, Wireshark, and Metasploit.tcpdump
###Databases and SQL
Core Concepts
- >Database: Organized data collection.
- >Relational Database: Tables connected by relationships.
- >SQL (Structured Query Language): Interacts with databases.
Key SQL Queries
- >
: Returns specified columns.SELECT - >
: Identifies the table.FROM - >
: Filters results based on conditions.WHERE
Joins in SQL
- >INNER JOIN: Matches rows in multiple tables.
- >LEFT JOIN: Includes all rows from the first table and matched rows from the second.
- >RIGHT JOIN: Includes all rows from the second table and matched rows from the first.
- >FULL OUTER JOIN: Combines all rows from both tables.
###Additional Notes
Penetration Testing Tools
- >Metasploit: Exploits vulnerabilities.
- >Burp Suite: Tests web app weaknesses.
- >John the Ripper: Password cracking.
Linux Package Management
- >A package is software used individually or as part of applications.
- >Package Managers: Tools for installation and management.
###Advanced Commands
- >
: Temporary elevated privileges.sudo - >
: Detailed documentation for commands.man - >
: Command summaries.whatis - >
: Searches command manuals.apropos
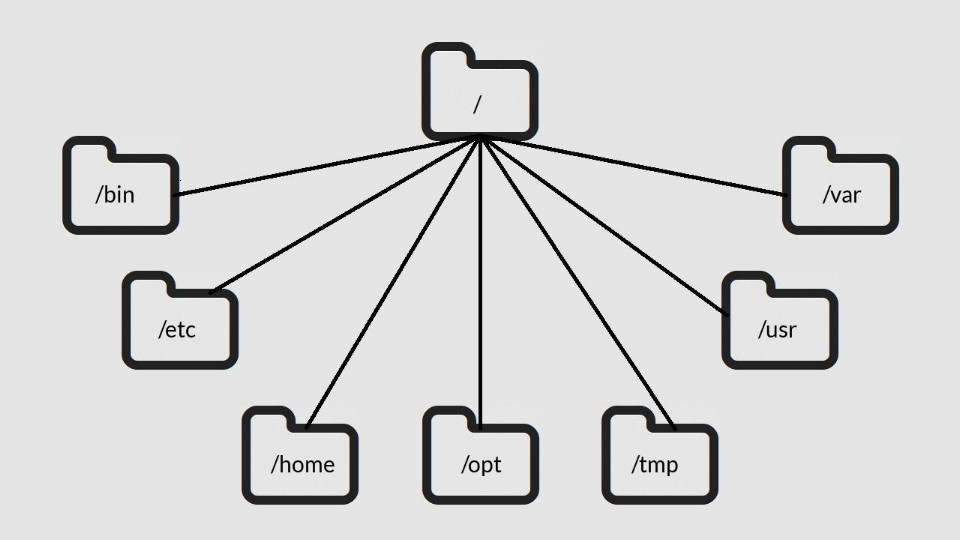
###File System Hierarchy in Linux
- >
Root (
): The top-level directory./ - >
Organizes directories and subdirectories.
- >
Example structure:
Linux Directory Structure
###Conclusion
Linux and its tools provide a flexible environment for various use cases, from development to cybersecurity. Mastering its commands, file systems, and interfaces opens pathways to efficient computing.