2024-08-1010 min read
Network and Network Security
Informational notes for Google Cybersecurity Professional Course - Network and Network Security.
###Networking Basics
Data Packet
A basic unit of information traveling across a network. It has three parts:
- >Header - Includes sender IP, destination MAC address, and protocol.
- >Body - Contains the data/content.
- >Footer - Includes receiving device information.
Bandwidth
The volume of data a device receives per second.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
An internet communication protocol that forms connections between devices to stream data.
IP (Internet Protocol)
A set of standards for routing and addressing packets during data transfer between devices.
Port
Software-based locations for sending and receiving data across a network.
- >Port 25 - Email
- >Port 443 - HTTPS
- >Port 20 - Large file transfers
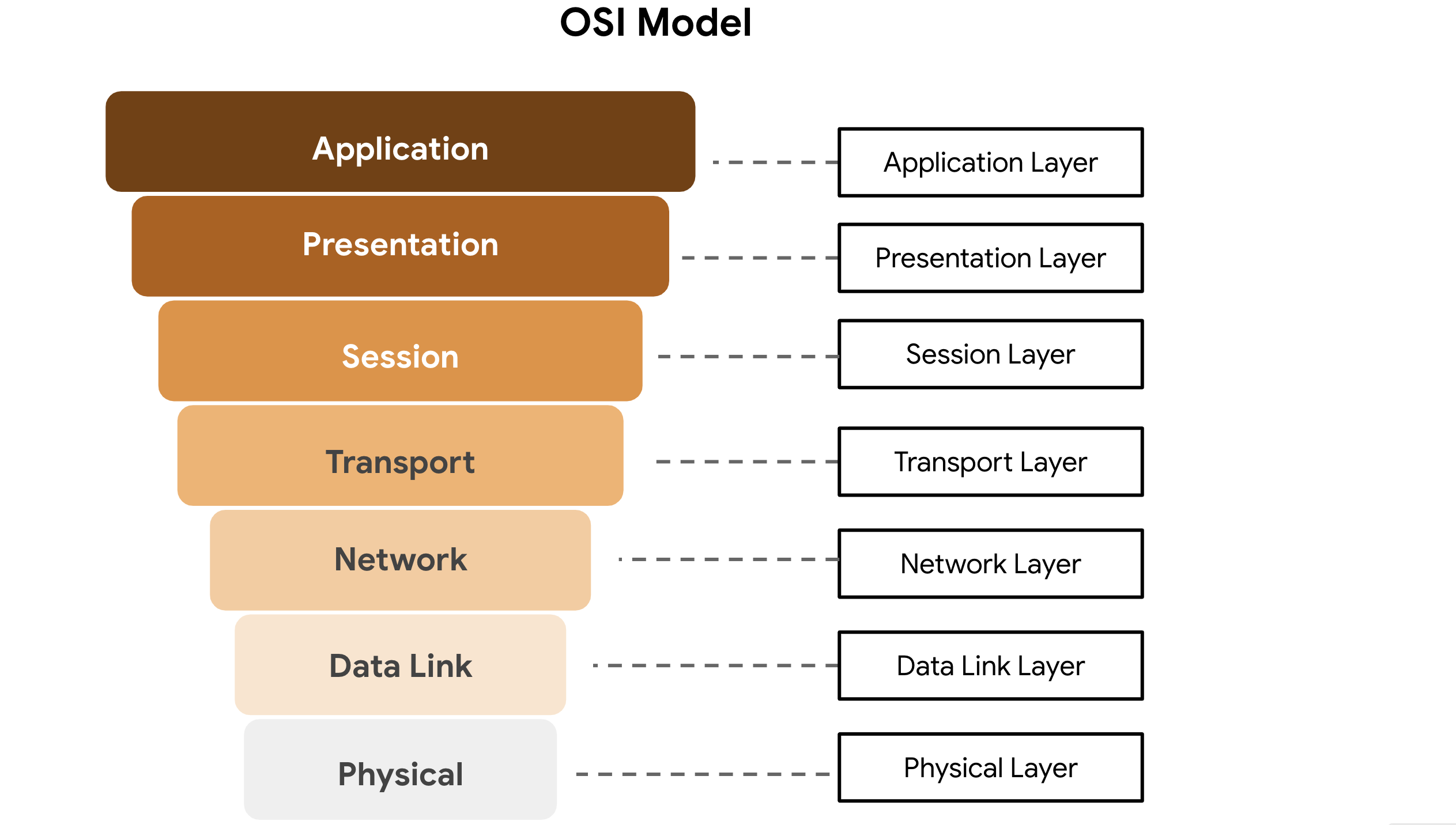
###TCP/IP Model
A framework for organizing and transmitting data across networks.
Layers:
- >Network Access - Handles packet creation and transmission.
- >Internet - Assigns IP addresses and connects networks.
- >Transport - Manages traffic flow and error control.
- >Application - Defines how data packets interact with devices (e.g., file transfers, emails).
Comparison with OSI Model
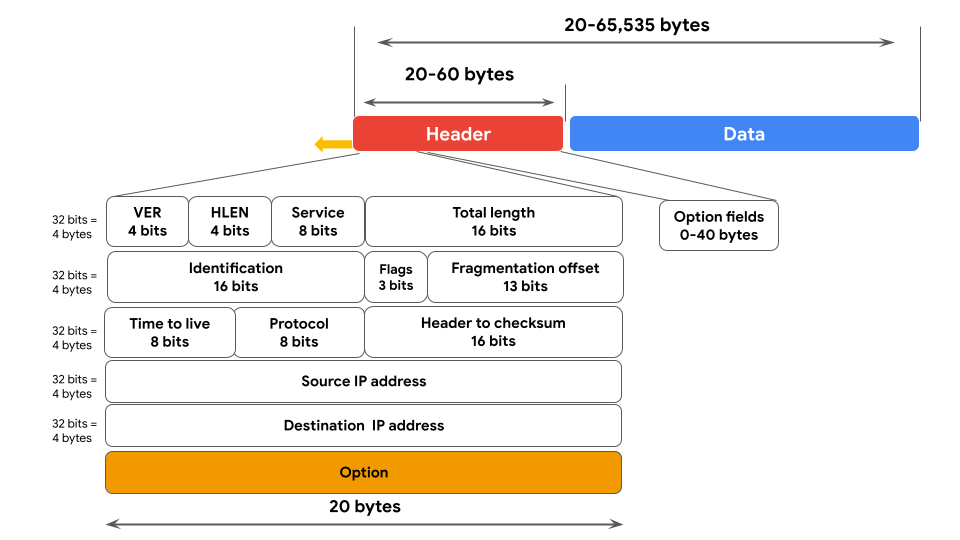
###IP Addressing
Types:
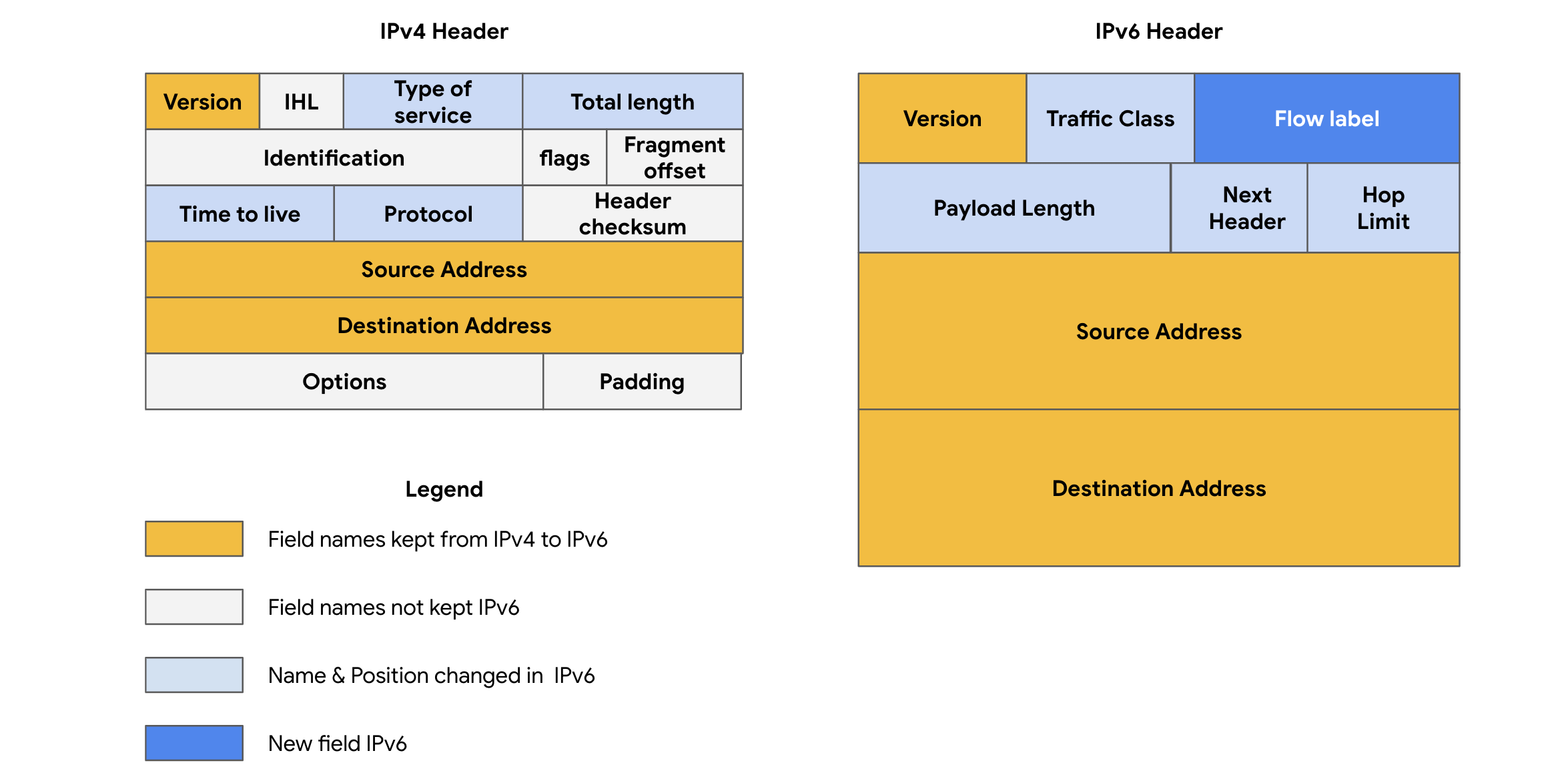
- >IPv4 - Uses decimal-separated numbers (e.g.,
).192.168.1.1
- >IPv6 - 32-character hexadecimal addresses for expanded device support.
Categories:
- >Public IP - Assigned by ISPs, visible to the internet.
- >Private IP - Used within local networks, invisible to the internet.
###MAC Address
Unique alphanumeric identifiers assigned to network devices.
- >Switches use MAC addresses to route packets efficiently.
###Network Protocols
Common Protocols:
- >ARP - Resolves MAC addresses.
- >HTTPS - Secure website communication.
- >DNS - Converts domain names to IP addresses.
- >ICMP - Reports transmission errors.
- >UDP - Fast but unreliable data delivery.
###Wireless Protocols
- >IEEE 802.11 (WiFi) - Wireless LAN standards.
- >WPA/WEP - Wireless security protocols for secure connections.
###Firewall and VPN
Firewall:
- >Types: Hardware, Software, Stateful, Stateless.
- >Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs): Incorporate advanced features like deep packet inspection and threat intelligence.
VPN (Virtual Private Network):
- >Encrypts data and masks IP addresses for secure communication.
###Subnetting and Proxy Servers
- >Subnetting: Divides a network into logical subgroups (subnets).
- >Proxy Servers: Forward or restrict internet traffic:
- >Forward Proxy - Controls user internet access.
- >Reverse Proxy - Regulates external access to internal servers.
###Network Attacks
DoS and DDoS Attacks:
- >SYN Flood - Overloads servers with SYN packets.
- >ICMP Flood - Excessive ICMP packets disrupt services.
- >Ping of Death - Oversized ICMP packets crash systems.
Packet Sniffing and Spoofing:
- >Passive Sniffing - Observes packets.
- >Active Sniffing - Alters packet contents.
- >IP Spoofing - Impersonates devices by faking IP addresses.
###Security Hardening
Focus Areas:
- >Hardware - Regular updates and strong physical security.
- >Operating Systems - Patch updates, strong passwords, MFA.
- >Applications - Frequent vulnerability assessments.
- >Networks - Encryption, port filtering, segmentation.
Penetration Testing:
Simulated attacks to identify vulnerabilities.
###Virtualization and Cloud Security
- >VMs and Sandboxes: Isolated environments for secure testing.
- >Cloud Hardening: Includes IAM, hypervisors, baselining, and cryptography.